The Japan Fair Trade Commission issues “Proactive Development of Competition Policy for Promotion of Innovation - Roles of the Japan Fair Trade Commission in Our Changing Times” based on the recognition that fostering innovation is essential for Japan to achieve sustainable economic growth and demonstrate its competitiveness.
Proactive Development of Competition Policy for Promotion of Innovation
- Roles of the Japan Fair Trade Commission in Our Changing Times -
January 28, 2026
Japan Fair Trade Commission
1. Introduction
The environment surrounding the Japanese economy is at a major turning point due to multiple waves of change, such as changes in the industrial structure due to rapid progress in digital technology and responses to climate change issues. At the same time, the Japanese economy faces various challenges, such as the shrinking domestic market and supply constraints due to a population decrease, a low birthrate, and an aging population, as well as the rising costs of raw materials. Even under these circumstances, in order for Japan to achieve sustainable economic growth and demonstrate its competitiveness in the international economy, it is important to improve the productivity of enterprises. For that, it is crucial to create innovation, particularly the creation of products and services that will contribute to solving issues not only in Japan but around the world. Based on the above recognition, the Japan Fair Trade Commission (JFTC) will develop competition policy with the aim of promoting innovation particularly by fostering an environment in which enterprises can demonstrate their ingenuity to the fullest extent while securing the interests of general consumers by promoting fair and free competition.The Japanese economy is now shifting from a “deflation and cost-cutting economy” to a “growth-oriented economy” with increasing investment toward growth and productivity improvement. Smooth price pass-through and continuous wage growth will lead to a virtuous cycle of economic growth, bringing vitality to the Japanese economy as a whole including small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), promoting investment, creating innovation, and improving the productivity of enterprises. Initiatives by the JFTC to ensure fairness in transactions are now essential for realizing a growth-oriented economy.
Another urgent issue is responding to the rapid changes in the economic and social environment surrounding Japan, including the promotion of initiatives toward advancement of a digital society, the realization of a green society, and the strengthening of economic security. As markets and industrial structures become increasingly complex and specialized, dialogue with stakeholders, etc. such as relevant enterprises and consumers will be more important than ever to promote fair and free competition. It is necessary not only to fill the gap between regulations and actual operations by accurately understanding the actual state of competition in each field through close dialogue with stakeholders, etc. but also to promote a competitive market environment that encourages innovation by enhancing predictability for enterprises.
Furthermore, to make these policies effective and create a foundation for real innovation, strict law enforcement against violations is indispensable as an underpinning policy. Business practices that unfairly disadvantage SMEs, etc. undermine the spirit of innovation, and exclusive conduct such as the establishment of exclusive trading conditions to exclude new entrants is an act that obstructs market renewal. Fixing prices and suppliers through cartels or bid-rigging are malicious acts as they undermine incentives for innovation. By strictly enforcing the Antimonopoly Act (AMA) against “forces that resist change”, which maintain these unjust business practices and create closed markets and fixed business relationships, the JFTC will continue to fulfill its fundamental mission of revitalizing the economy and promoting consumer interests.
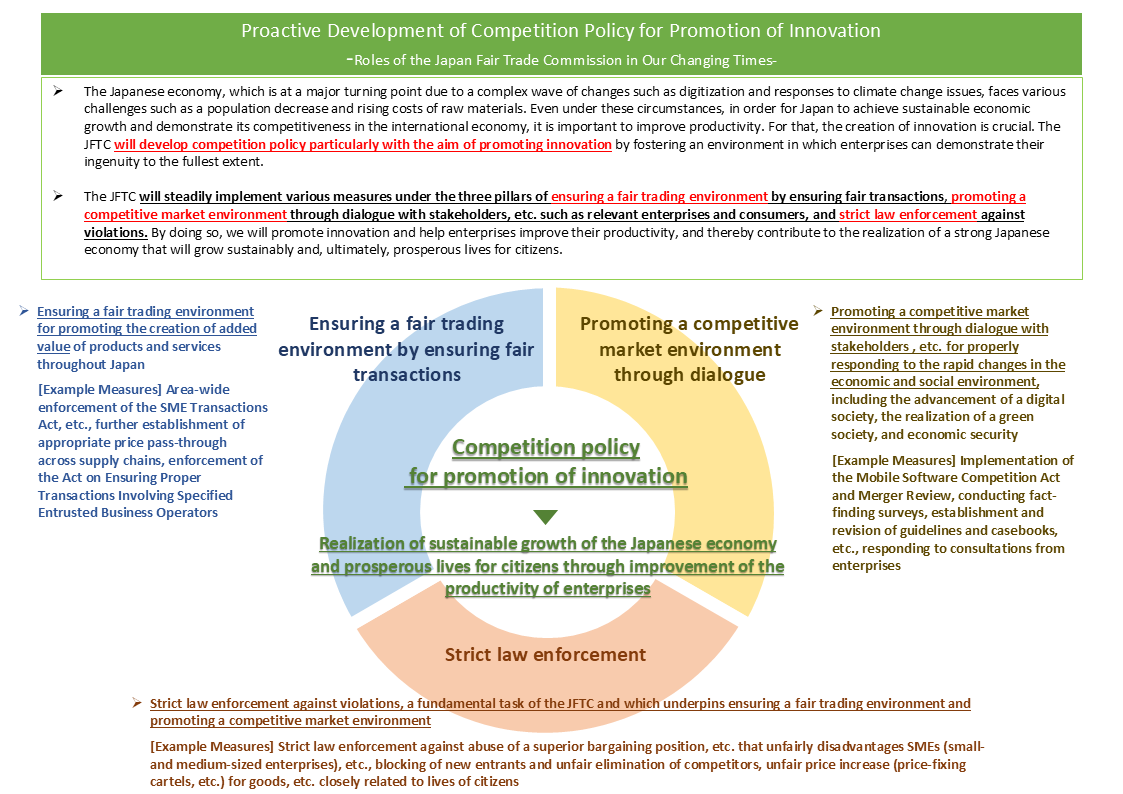
In order to fulfill the roles described above and to promote fair and free competition, the JFTC will steadily implement the specific measures set out in 2., below, under the three pillars of ensuring “a fair trading environment” by ensuring fair transactions, “promoting a competitive market environment” through dialogue with stakeholders, etc., and “strict law enforcement” against violations. Through the implementation of these measures, we will promote innovation and support the improvement of business productivity, thereby contribute to the realization of a strong Japanese economy capable of achieving sustainable growth and, ultimately, to prosperous lives for citizens.
2. Specific Measures
(1) Ensuring a fair trading environment by ensuring fair transactionsIn order for the Japanese economy to regain the power of innovation, maintain vitality, and continue to develop, it is necessary to review “the deflationary business practices” that have been formed over a long period of time. While innovation is brought by enterprises and the people who work there, a structure in which trading prices are left unchanged may discourage the behavior of both enterprises and workers, thereby potentially reducing the power of innovation and technological advancement. To promote innovation that creates added value with differentiated innovative goods and services, it is necessary to eliminate conduct that unfairly disadvantages SMEs (including startups), freelancers (business operators who undertake business as individuals), etc., such as abuse of a superior bargaining position, and to ensure a fair trading environment in which compensation commensurate with added value is paid under appropriate conditions. From the same perspective, it is also important to ensure fair trading involving intellectual property and know-how.
The Comprehensive Economic Measures to Build a “Strong Japanese Economy” approved by the Cabinet on November 21, 2025 also states “work to ensure price pass-through and fair transactions in order to help SMEs and small-scale enterprises secure resources to continue raising wages in excess of inflation.”
With a tough business environment marked by rising raw material and energy prices, the JFTC will proactively take measures against abuse of a superior bargaining position that unfairly disadvantages SMEs (including startups), freelancers, etc., as well as violations of the Act on Proper Transactions with Small and Medium-Sized Entrusted Business Operators (SME Transactions Act) and the Act on Ensuring Proper Transactions Involving Specified Entrusted Business Operators, and implement measures to prevent violations. By doing so, we will ensure a fair trading environment among enterprises, realize smooth price pass-through, and foster an environment in which all business operators, regardless of their business scale, can serve as drivers of innovation throughout Japan. Specifically, the JFTC will mainly implement the following measures for the time being, by combining advocacy and enforcement.
○ Eliminate business practices that impede smooth price pass-through and ensure fair transactions throughout Japan by promptly and effectively enforcing the SME Transactions Act that came into force in January 2026, Act on Ensuring Proper Transactions Involving Specified Entrusted Business Operators, and the AMA, and by disseminating the Guidelines for Price Negotiations for the Proper Transfer of Labor Costs. In addition, the JFTC will establish and strengthen a structure for cooperation with the Small and Medium Enterprise Agency and the relevant ministries with jurisdiction over respective businesses in order to realize area-wide enforcement of the SME Transactions Act.
○ Examine further measures for ensuring an environment conducive to appropriate price pass-through across the entire supply chains, for ensuring appropriate payment conditions, and against the issue of business practices related to logistics, for example, by reviewing and clarifying the views on abuse of a superior bargaining position.
○ Promote fair transactions involving intellectual property and know-how by conducting, for example, market studies on transactions related to intellectual property, know-how, and data, and considering formulating guidelines on the AMA based on the results of such surveys.
○ In the light of diversified working styles, proactively enforce the Act on Ensuring Proper Transactions Involving Specified Entrusted Business Operators, which entered into force in November 2024 in order to ensure an environment in which freelancers can engage in work in a stable manner.
○ Ensure a fair trading environment to support creators in the content industry, including films and animations, for example, by publicizing and disseminating concreate interpretations and approaches on the AMA and competition policy.
Ensuring fair transactions constitute the creation of a foundation that underpins the Japan-origin innovation by ensuring the circulation of funds throughout the entire supply chains. Through the foregoing initiatives aimed at ensuring fair transactions, we will secure a fair trading environment in which the seeds of innovation can grow regardless of business scale and region, including innovation by SMEs (including startups) and sole proprietors as well as large-scale enterprises, and innovation emerging not only from urban areas but also from regional communities.
(2) Promoting a competitive market environment through dialogue
In order to ensure the sustained generation of innovation, it is essential that the market environment is properly developed. As the Japanese economy faces a wide range of changes, including structural changes in market driven by digitalization and growing needs to promote the initiatives toward the realization of a green society that the Japanese economy faces, it is indispensable to engage in close dialogue with a broad range of stakeholders and other relevant parties and to accurately grasp the actual state of competition in each sector for the development of a market environment that fosters innovation.
For example, in the digital field, market structures tend to become monopolized or oligopolized due to factors, such as indirect network effects derived from multi-sided markets, making new entry less likely to emerge. Considering this situation, the Mobile Software Competition Act was enacted in June of 2024 and entered into full enforcement in December 2025, with the aim of promoting a competitive market environment in order to stimulate innovation by various enterprises through competition and enable consumers to select and enjoy the benefits of various services resulting from such innovation, with respect to specific mobile software. We will effectively implement the law in order to realize a competitive environment in the mobile software field, while accurately understanding the actual state of markets through continuous dialogue with a wide range of market participants and stakeholders, including the designated providers, relevant business operators, and relevant ministries, cooperating with overseas competition authorities and specialists, etc. in the digital field, while appropriately taking into account security, privacy, youth protection, and other key concerns. In addition, we will promote a competitive market environment so that innovation will not be unduly nipped in the bud in the digital field while closely monitoring market trends related to new technologies such as generative AI by deepening dialogue with market participants, etc.
Looking at the other fields, for example, in relation to sustainability, there is an urgent need to strengthen initiatives toward climate change issues internationally, and enterprises in Japan are also taking initiatives regarding climate change issues. Given this, we will encourage innovation by enterprises toward the realization of a green society by proactively responding to consultations from enterprises, etc. in light of the “Guidelines Concerning the Activities of Enterprises, etc. Toward the Realization of a Green Society under the AMA” revised in April 2024. Additionally, we will continue to review the guidelines on based on changes in markets and business activities as well as specific cases of law enforcement and consultation, etc.
While strengthening of economic security is required in Japan, supporting the creation of products and services that help ensure Japan’s autonomy and indispensability by promoting innovation by various enterprises through competition will also contribute to strengthening of economic security. When strengthening economic security, it is also important to clarify cases where an enterprise’s initiative does not pose a problem under the AMA. For that purpose, the JFTC published “Basic Approach to the Antimonopoly Act for Business Activities Related to Economic Security” and the “Casebook on Economic Security and the Antimonopoly Act” in November 2025 and will proactively respond to consultations from enterprises, etc. Through these initiatives, the JFTC will facilitate consultations with it, resolve compliance concerns of enterprises through individual consultations, etc., and support efforts of enterprises toward strengthening of economic security.
In this way, the JFTC will ensure predictability for enterprises and promote a competitive market environment that promotes innovation by effectively implementing the Mobile Software Competition Act and merger review, conducting fact-finding surveys, establishing and revising guidelines and casebooks, etc., and responding to consultations from enterprises, while accurately understanding the increasingly complex and specialized changes in the economy through dialogue with stakeholders, etc.
(3) Strict law enforcement
The AMA stipulates basic rules that enterprises are to observe when conducting their business activities in a free market economy. It is necessary to strictly enforce laws against violations of the AMA, as these impede fair and free competition, and enforcement of the AMA is the most fundamental task entrusted to the JFTC. Strict law enforcement has the power not only to eliminate violations but also to break unfairly entrenched business relationships and practices and provide a powerful boost to innovation. Given the fact that ensuring a fair trading environment by ensuring fair transactions and promoting a competitive market environment through dialogue with stakeholders, etc. can be facilitated by ensuring strict enforcement of the AMA, it can be said that strict law enforcement underpins these two pillars.
To encourage the free ingenuity of enterprises and prevent innovation from being unduly nipped in the bud, the JFTC will proactively engage in law enforcement that supports initiatives for ensuring a fair trading environment and promoting a competitive market environment as well as law enforcement related to issues that have a significant impact on the lives of citizens such as rising prices, as follows.
○ Strict law enforcement against unfair business practices (such as abuse of a superior bargaining position) that could unfairly disadvantage SMEs (including startups), freelancers, etc., and make it difficult for them to conduct business activities aimed at innovation
○ Strict law enforcement against actions that obstruct market renewal and impede innovation, such as blocking of new entrants or unfair elimination of competitors
○ Strict law enforcement against price-fixing cartels and bid rigging, in which prices are raised in concert and unfair attempts to maintain resale prices, for goods and services closely related to the lives of citizens
The strict law enforcement set forth above will continue to be carried out in effective cooperation, leveraging the strengths of advocacy and enforcement.
3. Organizational Reform
In order to steadily implement these specific measures and fulfill the roles of the JFTC necessary for the sustainable growth of the Japanese economy, we will shift to an optimized organizational structure that is sustainable in the medium to long term, according to the characteristics of the three pillars: ensuring a fair trading environment, promoting a competitive market environment, and strict law enforcement. To this end, we will review the existing structure, including at the departmental/bureau level, and reorganize and strengthen the structure so that respective organizations can implement specific measures flexibly and effectively while cooperating organically. Also, in rural areas, to ensure a sound competitive environment and revitalize local economies, it is necessary not only to disseminate ideas on competition policy through public relations activities concerning the AMA, the SME Transactions Act, and the Act on Ensuring Proper Transactions Involving Specified Entrusted Business Operators, but also to carefully enforce laws against violations that unfairly disadvantage SMEs and freelancers, etc., such as abuse of a superior bargaining position. The JFTC will strengthen the structure of its regional offices so that specific measures can be implemented throughout Japan.At the same time, we will work to secure and enhance human resources who will play the pivotal roles of the JFTC and will systematically secure and develop human resources with expertise who are capable of responding to changes in the economic and social environment. In addition, we will work to make effective use of human resources by streamlining our activities through proactive use of the latest digital technologies.
Going forward, the JFTC will strive to secure and enhance the necessary personnel and structure.






